I’d argue for moderation.
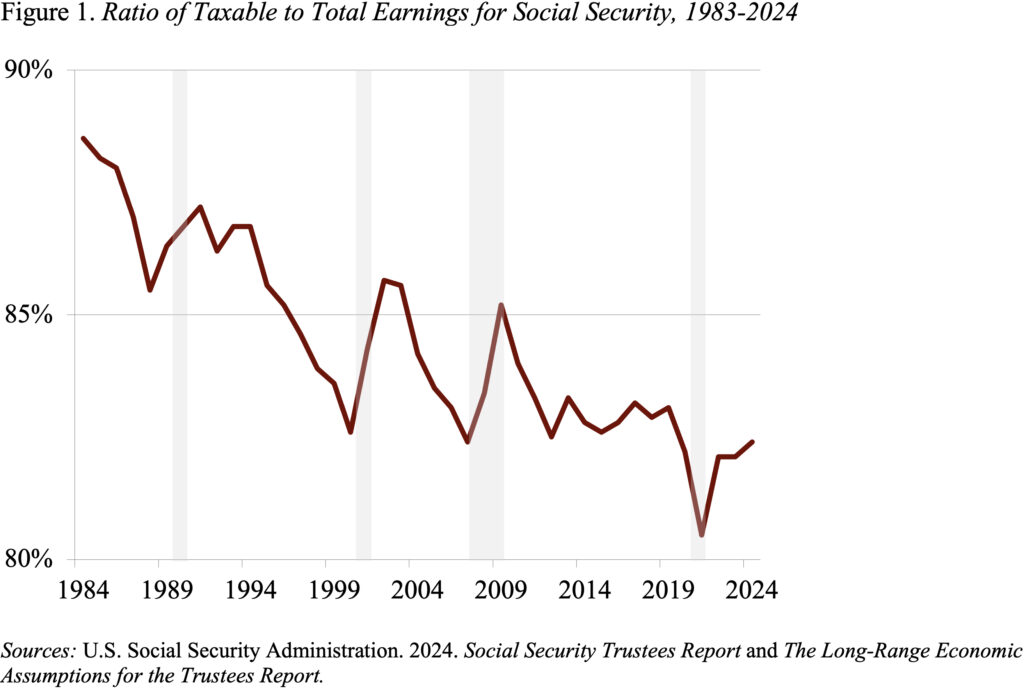
I normally have a powerful opinion on points in my sphere, however have been going backwards and forwards about one element more likely to be in any package deal to repair Social Safety – particularly, growing the taxable wage base. Some enhance within the wage base is sort of inevitable as a result of rising wage inequality has prompted the share of wages topic to taxation to say no sharply because the final main piece of laws in 1983 (see Determine 1).
The minimalist choice is solely to boost the taxable restrict from $168,600 in 2024 to an quantity that may make sure that 90 p.c of wages have been topic to the payroll tax – roughly $300,000. Probably the most aggressive choice could be to take the restrict off altogether and supply no further advantages. In between are choices that take away the restrict and supply advantages of varied generosity.
As background, it’s useful to grasp how advantages are presently calculated. Step one is to calculate the employee’s common listed month-to-month earnings (AIME), which entails adjusting the employee’s wage historical past for will increase within the common wage stage, deciding on the best 35 years, and taking the month-to-month common. The second step is to use the profit method (see Desk 1) to calculate the employee’s major insurance coverage quantity. (The odds within the profit method are mounted by legislation, however the greenback ‘bend factors’ are adjusted every year for adjustments within the nationwide common wage index.) Lastly, the first insurance coverage quantity is adjusted actuarially for early or late claiming.

The Social Safety actuaries put out a beautiful booklet that accommodates greater than 150 choices for closing the 75-year deficit by both reducing advantages or elevating further income. Desk 2 summarizes 5 of the 19 choices for growing the taxable wage base. For context, the 2024 Trustees Report projected Social Safety’s shortfall over the following 75 years to be 3.50 p.c of taxable payrolls.

Clearly, the most important monetary acquire comes from eliminating the taxable most – Choices, 3,4 and 5. I don’t like Choice 5 as a result of it dissolves any hyperlink between payroll tax contributions and advantages, which in the long term might undermine help for this system. Choice 3 appears too beneficiant to excessive earners, and the good points to Social Safety would decline over time as persistent wage inequality results in fast progress in advantages among the many excessive earners. Subsequently, the selection to me comes all the way down to elevating the cap to cowl 90 p.c of earnings or eliminating the cap and including a 3-percent bracket to the profit method (Choice 4).
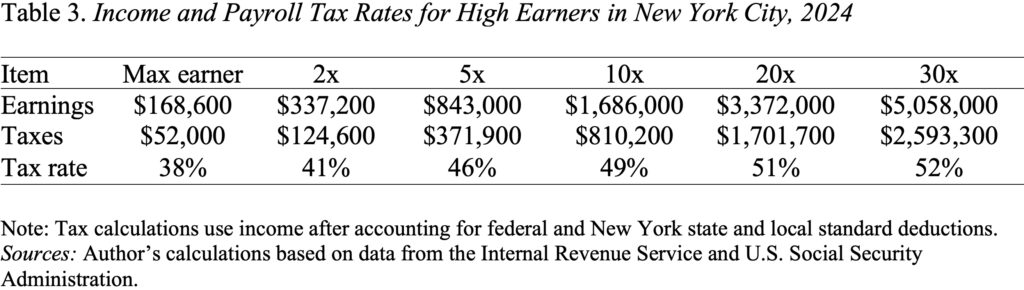
The selection then comes all the way down to how way more can we need to tax excessive earners. My colleague Ray Madoff on the Boston Faculty Legislation College makes a convincing case that prime earners – that’s, individuals who get all their earnings within the type of wages and salaries – pay their full share of taxes. Certainly, a fast calculation for these residing in New York Metropolis suggests that actually excessive earners pay greater than half their compensation in earnings (federal, state, and metropolis) and payroll taxes (no taxable most on the Medicare tax plus a 0.9-percent tax on earnings above $200,000 for singles and $250,000 for married {couples}) (see Desk 3). I do know New York is on the excessive aspect by way of taxes, however that’s the place I get most of my complaints from!
In the long run, some mixture of Choices 1 and a pair of looks as if the way in which to go – elevate the taxable wage base to cowl 90 p.c of earnings and credit score a small share (maybe 3 p.c) of the earnings in direction of advantages. The large choice for me was not taking the cap off altogether. Thanks for serving to me work by way of my dilemma.

